Prioritizing tasks, projects, or any other work items isn’t always easy.
Why?
Because there are often conflicting factors to consider. Its value to the end user, how much it’ll cost to complete, and how long it’ll take are just a few examples.
Fortunately, there’s a way to objectively prioritize your work.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the ins and outs of the RICE prioritization framework. We’ll show you what it is, how it works, and how to use it to prioritize your work effectively.
What is RICE prioritization?
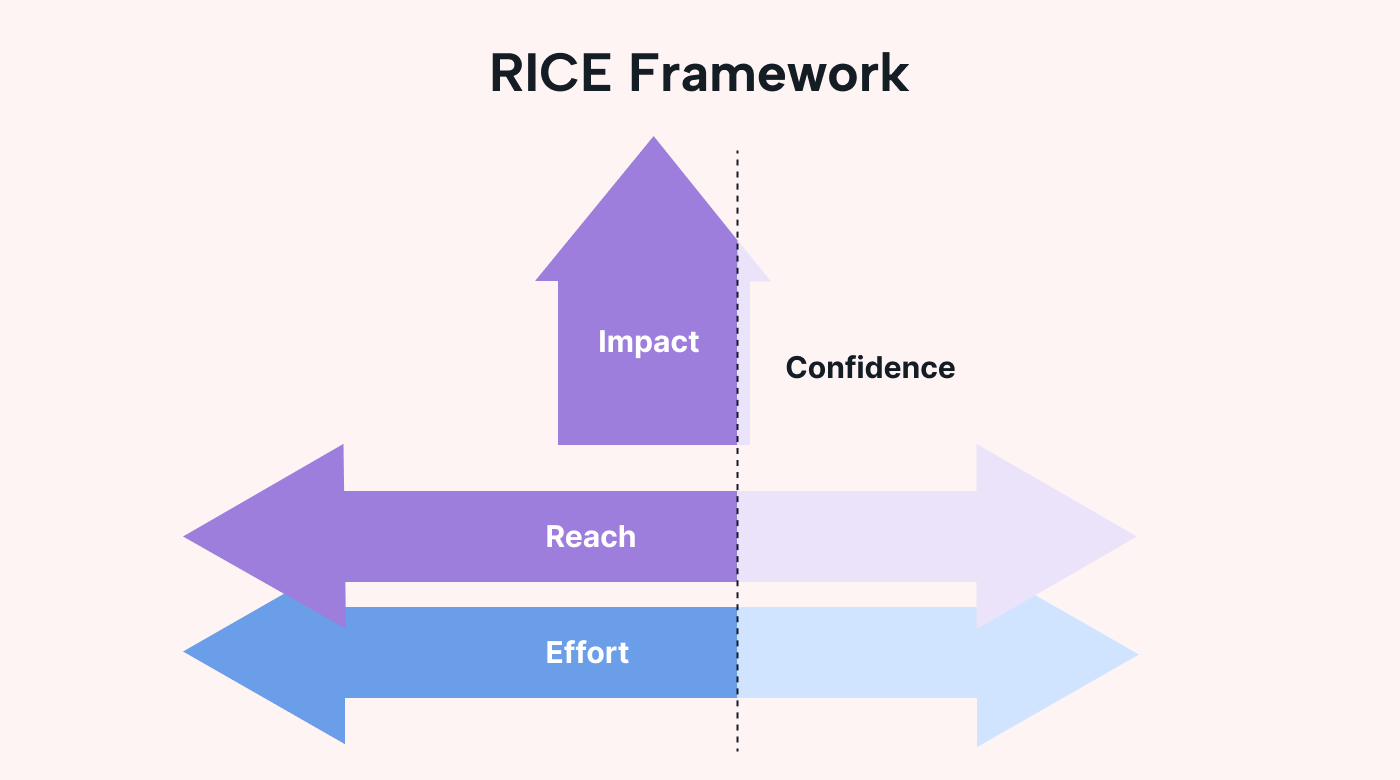
RICE is an acronym for reach, impact, confidence, and effort. It’s a framework for prioritizing projects, tasks, or initiatives based on their potential impact, required resources, confidence level, and effort involved.
 |
With this framework, you can make better-informed decisions about which tasks, products, or projects to prioritize based on their potential impact, feasibility, and resource allocation. So instead of taking a stab in the dark and hoping for the best, you can figure out exactly what areas of work you should be prioritizing (and why they’re important).
Take a look at this example of RICE prioritization to see it in action.
What are the components of the RICE framework?
Let’s look at each of the RICE components in more detail.
- Reach. Reach refers to the number of people or users who will be affected by the project or task. It helps determine the potential audience or customer base impacted by the project. Let's say you’re implementing a new feature in a mobile app. If the feature is relevant to all app users, the reach would be high. But if it's only applicable to a specific subset of users, the reach would be lower.
- Impact. Impact measures the potential benefit or value that the project or task will deliver if the work is successfully implemented. Suppose you're planning to optimize your website's checkout process. In this situation, you could measure the impact in terms of conversion rate, revenue generated, or customer satisfaction. If the optimization is expected to increase the conversion rate by 10% and generate a big boost in revenue, the impact would be high.
- Confidence. Confidence represents the level of certainty in the data used to assess reach and impact. For example, imagine that you’re launching a marketing campaign to target a new audience. If you have extensive research and data supporting the potential success of the campaign (such as market research, competitor analysis, or feedback from a focus group), the confidence would be high. If there’s limited data or the market is uncertain, you might have low or medium confidence.
- Effort. Effort estimates the resources and time required to complete the project or task. It considers factors such as development time, cost, and complexity. Let’s use product development as an example. If you’re planning to launch a new product feature, the level of effort is based on the amount of time it’ll take to make, the number of product developers you’ll need, and any other resources required. If the feature were relatively simple and could be implemented quickly, the effort would be low. If it requires extensive testing, the effort would be high.
What is the RICE method formula?
The RICE formula involves assigning numerical values to reach, impact, confidence, and effort. Here’s how it works:
- Reach is usually the actual number of people you plan to reach by completing the task or initiative. For example, if a new software feature would be used by 1,000 people, your reach score would be 1,000.
- The impact and effort scores are usually on a scale from 1 to 10, indicating the relative magnitude or importance (with 10 being the most important).
- Confidence is usually a percentage, where 100% shows total confidence and 0% shows none. The confidence score will impact the numerical scores of the other areas of the formula. For example, if the confidence score is low, it can reduce the numerator value of reach, impact, and effort.
To calculate the RICE score, you multiply the reach, impact, and confidence scores, then divide the result by the effort score:
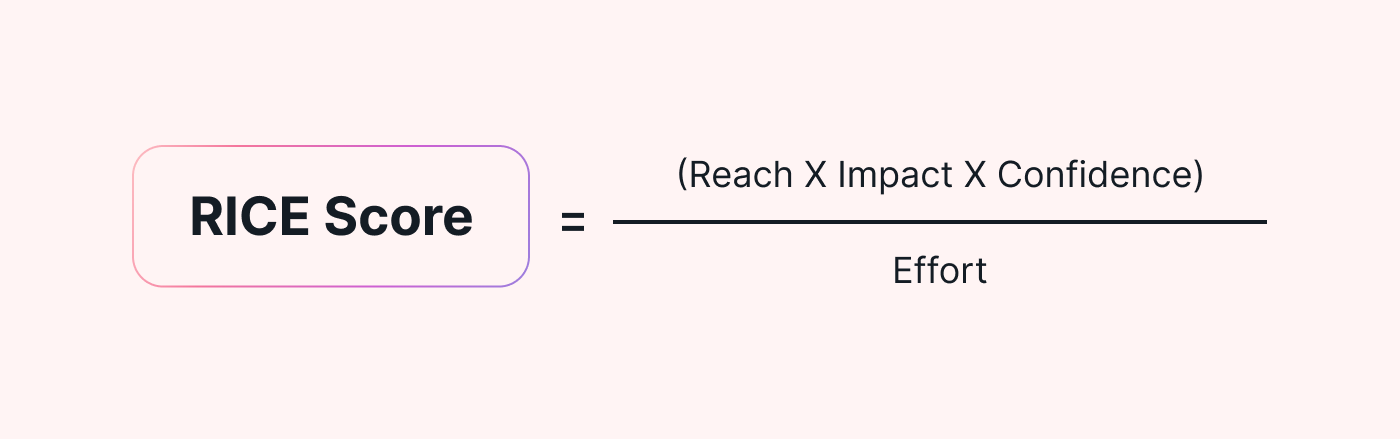 |
The higher the RICE score, the higher the priority of the project or task.
What is an example of RICE prioritization?
Imagine you’re a product manager at a software company. You have two potential features to prioritize for the next development cycle — enhanced search functionality or a new dark mode.
Here's how you might evaluate two features using the RICE scoring system:
Feature 1: Enhanced search functionality
- Reach score: 5,000
- Impact score: 8
- Confidence score: 70%
- Effort score: 5
RICE score = 5,000 x 8 x 70 / 5 = 560,000
Feature 2: Dark Mode
- Reach score: 2,000
- Impact score: 6
- Confidence score: 80%
- Effort score: 2
RICE score = 2,000 x 6 x 8 / 2 = 48,000
Based on these scores, enhanced search functionality is a bigger priority than dark mode.
What are the pros of RICE prioritization?
The RICE framework helps teams in a variety of ways. Take a look at some of the benefits below:
- Make objective, informed decisions. The RICE scoring model provides a structured and quantitative approach to prioritization. It removes personal biases and subjective opinions by relying on measurable factors, helping you make informed decisions about your business activities.
- Enhance communication and collaboration. With the RICE framework, you have clear language for discussing and evaluating priorities. As a result, everyone understands how to identify top-priority tasks and the criteria for doing so. Plus, if you use an online tool like Motion to manage your priorities, you can easily communicate about the RICE framework with your team by sharing updates, adding comments to tasks, and asking questions.
 |
- Improve resource allocation. By considering the resources required to complete a project or task, RICE helps teams allocate resources effectively. As a result, you can be sure that your resources are being used effectively.
Are there any downsides?
Now that we know the benefits of using the RICE framework for prioritization, let’s look at some of the challenges you might face — and how to overcome them.
- Subjectivity in scoring: Assigning scores involves some level of subjective judgment. People have different interpretations or biases when assessing the factors in the RICE model, which can lead to inconsistent scoring and skewed results. To avoid this, it helps to have multiple people involved in the score-creation process. That way, you take different perspectives into account.
- Difficulty in quantifying qualitative factors: The RICE framework provides a quantitative approach to prioritization. But some factors are hard to quantify, such as user experience or strategic importance). Again, collaborating with colleagues can make this easier. When you have multiple people involved in the process, you’ll get a better idea of how to quantify these areas as accurately as possible.
- Overlooking dependencies: RICE evaluates alternatives without considering any dependencies between them. For example, certain features or tasks may rely on other features or tasks finishing before they can begin. Prioritizing them solely based on RICE scores may overlook critical relationships or dependencies that can have a massive impact on project success. To overcome this problem, you need to be aware of dependencies alongside any RICE evaluations. That way, you can make sure that any key dependencies aren’t overlooked when prioritizing your work.
How to use the RICE framework to prioritize your work
If you’re thinking about using the RICE model to prioritize your work, here are the steps you can follow to use it effectively.
Define and score the RICE criteria
The first step to successfully using the RICE framework is to determine the scoring system or scale for each criterion. For example, you can use a scale of 1–10, 1–5, or anything else that works for you and your team.
When it comes to scoring your RICE criteria, be sure to work with your teammates. As we’ve already mentioned, if just one person is in charge of scoring tasks, the results can be skewed to their perspective. By including some of your colleagues in this process, you’ll make sure you have a more accurate scoring system.
When you know what your RICE scoring criteria will be, you can now outline all the features or products that you want to score. Then, you’ll move on to calculating the score for each item, which leads us nicely to our next step.
Calculate the RICE score
After assigning criteria, you can now calculate your RICE score for each feature or product that you want to prioritize. Use the RICE calculation from above to get your RICE score for each item.
Ideally, you should perform your calculations in a shared location. Why? For two reasons:
- It makes it easier to collaborate with your teammates.
- It provides a safe location for you to store all your calculations.
An online platform like Motion is a good example of a platform for creating and storing your RICE calculations. With our collaborative software, teams can access key project information from wherever they are in real time.
 |
This means that you can calculate your RICE scores in a centralized location that’s easily accessible. Plus, your teammates can add their own thoughts and suggestions by adding notes and tagging other users.
In other words, it makes it easy for everyone to work together and gives you a place to store all your RICE calculations for future reference. You never know when you might want to reflect on previous calculations to inform your business decisions.
Prioritize based on RICE scores
You have your RICE scores in place. Now you can select projects or assign tasks to your team based on which products or features the RICE scores said are more important. Remember — higher scores indicate a higher priority.
To make it easy to visualize the priority level of each task, consider using a platform like Motion. You can easily assign tasks a priority level, allowing you to instantly identify which tasks are the most important.
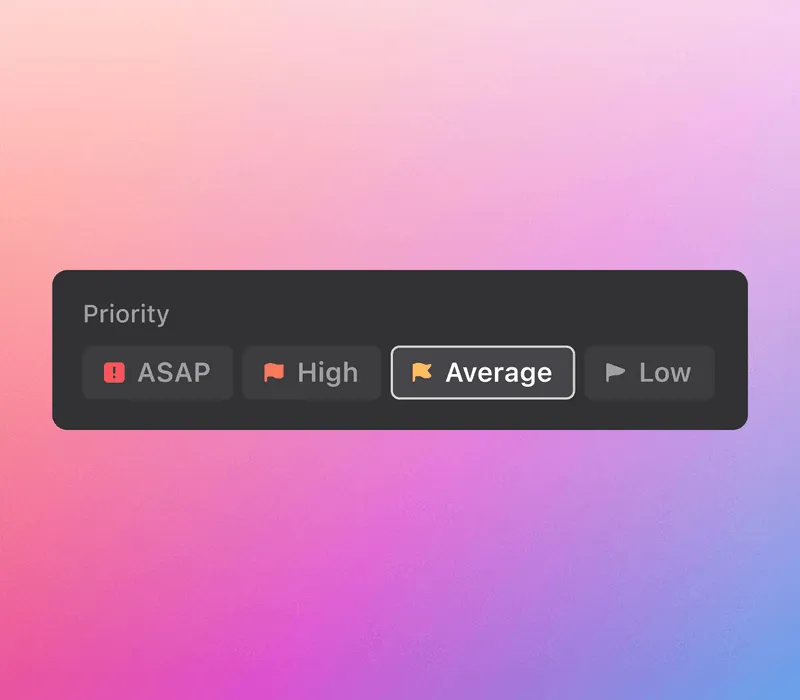 |
And when you add these to our AI-powered calendar, we’ll automatically put the top-priority tasks ahead of everything else.
After categorizing your tasks, share this information with your project team to ensure that everyone’s on the same page. If there are any questions or concerns about the order of priority, use this as an opportunity to incorporate their feedback and answer their questions.
For example, if the marketing team is concerned about the number of top-priority tasks that are coming their way, you can discuss this with them and identify whether:
- They have the capacity to perform the work
- They agree that the items you’ve prioritized are the most important tasks
Hopefully, you shouldn’t have to deal with many queries or concerns at this stage. If you include the relevant people in the scoring process, the items should already be prioritized with all these concerns in mind.
Review and adjust
At this stage, you can take a step back and consider any additional factors, constraints, or dependencies that may influence the order of tasks. Then, you can make adjustments to get your items in the right order.
This is another example of how Motion can be helpful throughout this process. With our platform, you can easily shuffle and reprioritize tasks with our drag-and-drop feature.
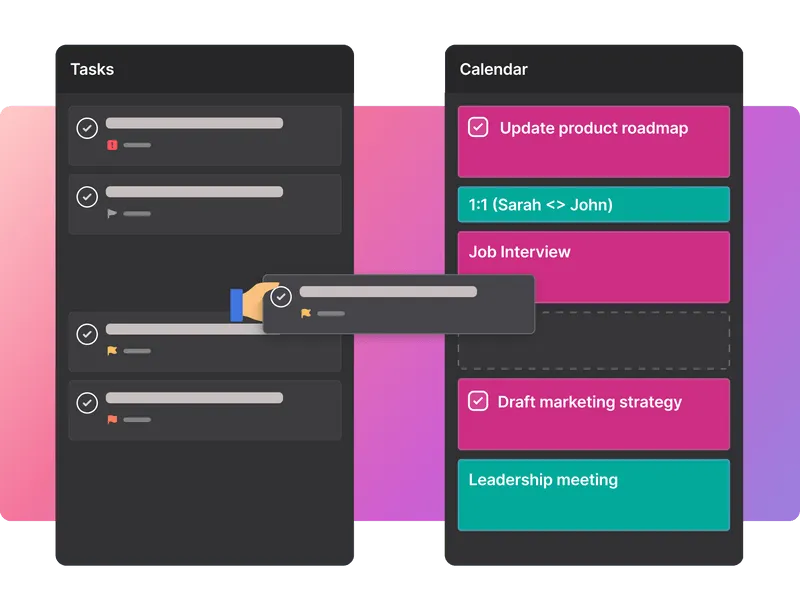 |
This makes it faster and easier for you to rearrange the order of your items. As a result, you can spend more time working on tasks to achieve your goals and less time manually juggling priorities.
Prioritize your products and features with RICE and Motion
Prioritizing tasks is an important part of any project, no matter the topic. With the RICE framework, you can objectively identify the top-priority features or products to work on. Motion can help you allocate your resources as effectively as possible, because you can assign and prioritize tasks according to their RICE importance.
If you want to improve your prioritization, use Motion’s calendar to prioritize tasks automatically. If you need to change your project schedule, our calendar will ensure your most important tasks come first. Sign up for a free trial today.





