For a project to succeed, it has accomplish its business goal and also meet two other requirements. It needs to be completed on time and within budget. Those seem reasonable enough, particularly in the context of a business venture, when time and money are precious. Yet, according to the Project Management Institute, nearly half of projects fail to meet those simple standards.
The critical path method (CPM) was one of the first tools developed in the discipline of project management. Despite its relative age, using the CPM can make the difference between planning a successful project and setting unmeetable deadlines.
In this article, we’ll explain the critical path method in simple terms. We’ll also discuss how to use it in your own projects, so you always successfully meet your deadlines.
What is the critical path method?
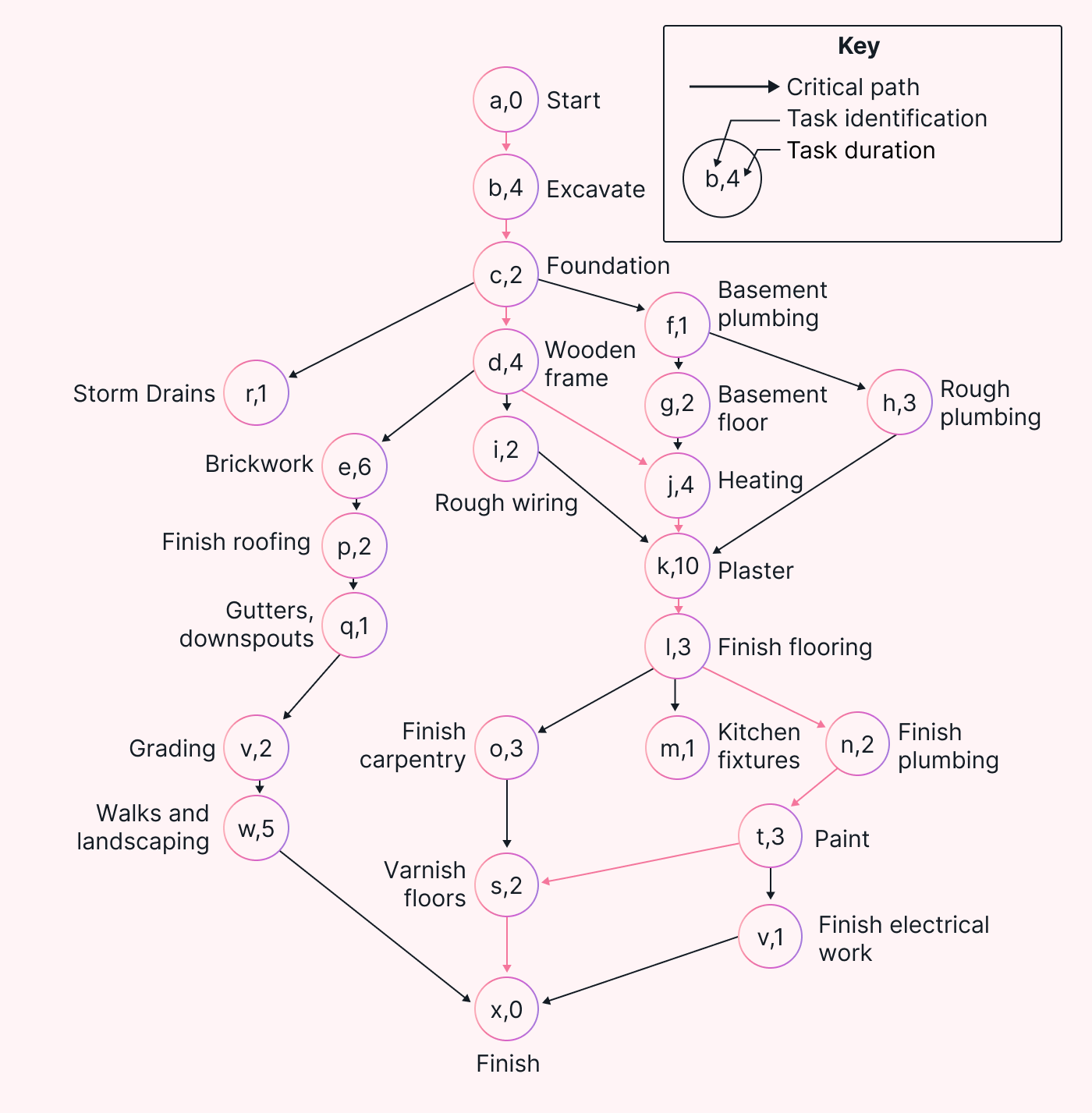
The definition of the critical path method may seem counterintuitive at first glance. It identifies the ‘path’ in a project, or linked set of dependent tasks, that takes the longest to complete.
Here’s a sample building project with the critical path shown as red arrows. By determining this path, you can calculate the minimum length of time the entire project will take. Let's break down each part to understand that more clearly.
Tasks
A project task or activity is fairly straightforward to understand. It's one step in a multi-step project. A classic example of working with the CPM is building a house. One task in house building might translate to laying a foundation, stringing electrical wire, or making the frame.
Dependent
A dependent task can only be started once another task is completed. In our house-building example, you can only build a frame once the foundation has been laid. Therefore, framing the building depends on the foundation being completed. There are other types of dependencies, but this is the most common.
Path
You can link dependent tasks together in order. For example, house building might include a path between laying the foundation, putting up the framing, adding the wiring, and so forth until the house is complete.
Most projects have multiple paths that diverge and converge. Nearly every task in house building depends on laying the foundation, but plumbing and wiring don't necessarily depend on each other. Therefore, each has a separate path.
Critical Path
Some paths take longer to complete than others. The 'longest' path is the one that takes the most time to complete. This is the critical path as it determines the minimum time required for the overall project.
Returning to our house-building example, all the landscaping tasks, or the landscaping path, may be completed fairly quickly. However, the much more time-consuming path of laying the foundation, framing, drywalling, and roofing determines how long the project will require.
Knowing how long it'll take to complete the landscaping is helpful. However, understanding the much longer critical path allows you to determine time requirements for the entire project schedule. Complex projects may have multiple critical paths. In addition, the critical path may change as tasks are adjusted, removed, or added.
Why is the CPM important to project management?
The critical path method's primary use is in scheduling. Not only will it allow you to determine the minimum time needed to complete the project, but it also allows you to schedule individual tasks. It also clarifies dependent relationships, so you know what else you must complete before starting each task.
The critical path method identifies the critical tasks to meet your deadlines. The tasks that aren't on the critical path have more flexibility. CPM, therefore, reveals where to focus your efforts, to reduce the overall project time requirements. Each aspect can improve your chances of completing a project successfully.
Note that 'method' in this case predates the idea of project management methodologies. CPM is a tool that can be used within many project management methodologies but doesn't make up a whole PM methodology itself.
Important terms for the CPM
There isn’t a lot of technical jargon to learn to apply the critical path method. However, understanding a few key terms will make using the critical path method much easier.
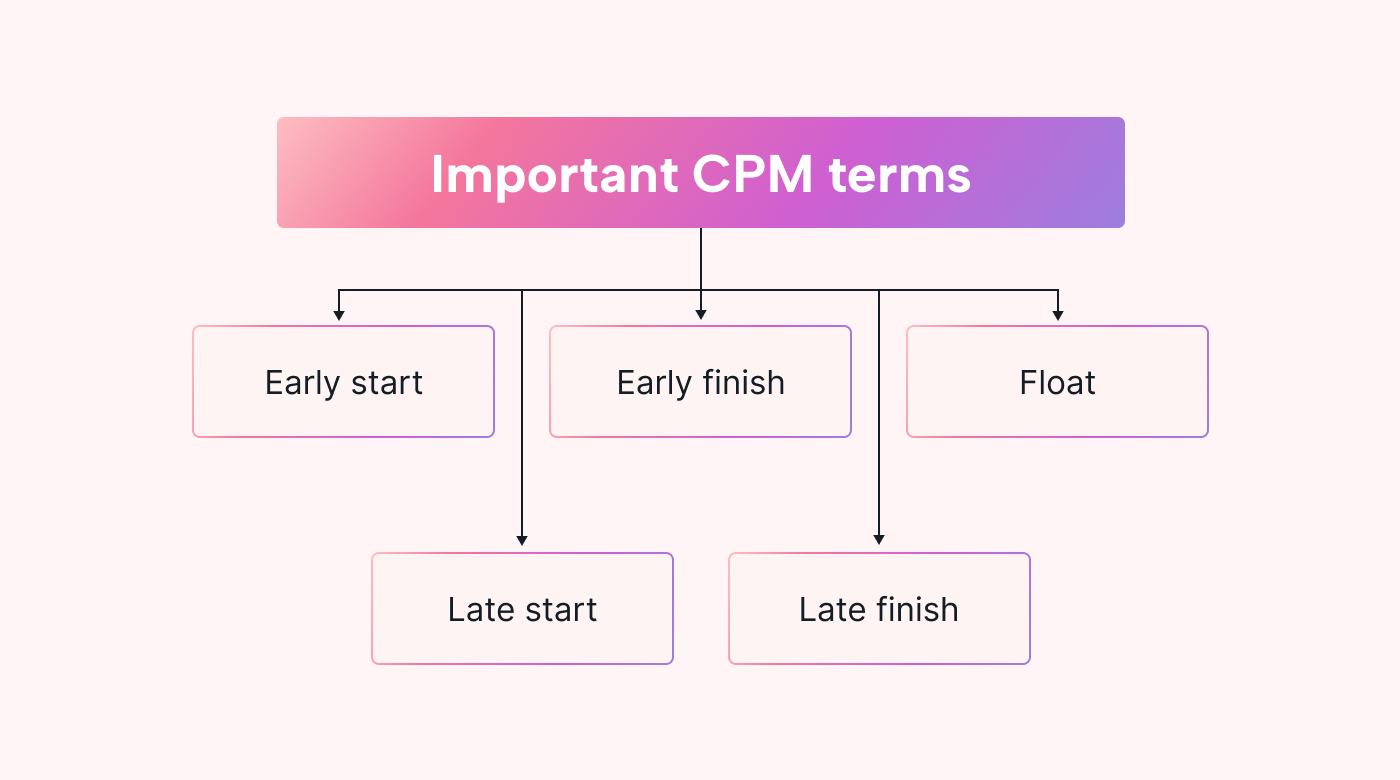 |
- Earliest start time - The earliest you can start each task. This may be affected by deadlines for previous tasks in a path.
- Late start - The latest a task can begin without delaying the overall project. It's also possible to use a critical path analysis to work backward. Doing this establishes the latest a project can start and still be completed on time.
- Earliest finish time - The earliest a task might be finished, considering estimated time requirements and those of previous tasks it depends on.
- Late finish - The latest a task might be completed without delaying the overall project.
- Float - Broadly, the difference between the early and late start and finish times. In other words, how long a task can be delayed without delaying the project. There are two types, free float, and total float.
How to find the critical path
Many apps out there'll help you determine the critical path, particularly for complex projects with many tasks. However, it's important to understand how the critical path is found, so you can make sure the software is doing its job correctly. For small projects, doing it by hand may also be helpful.
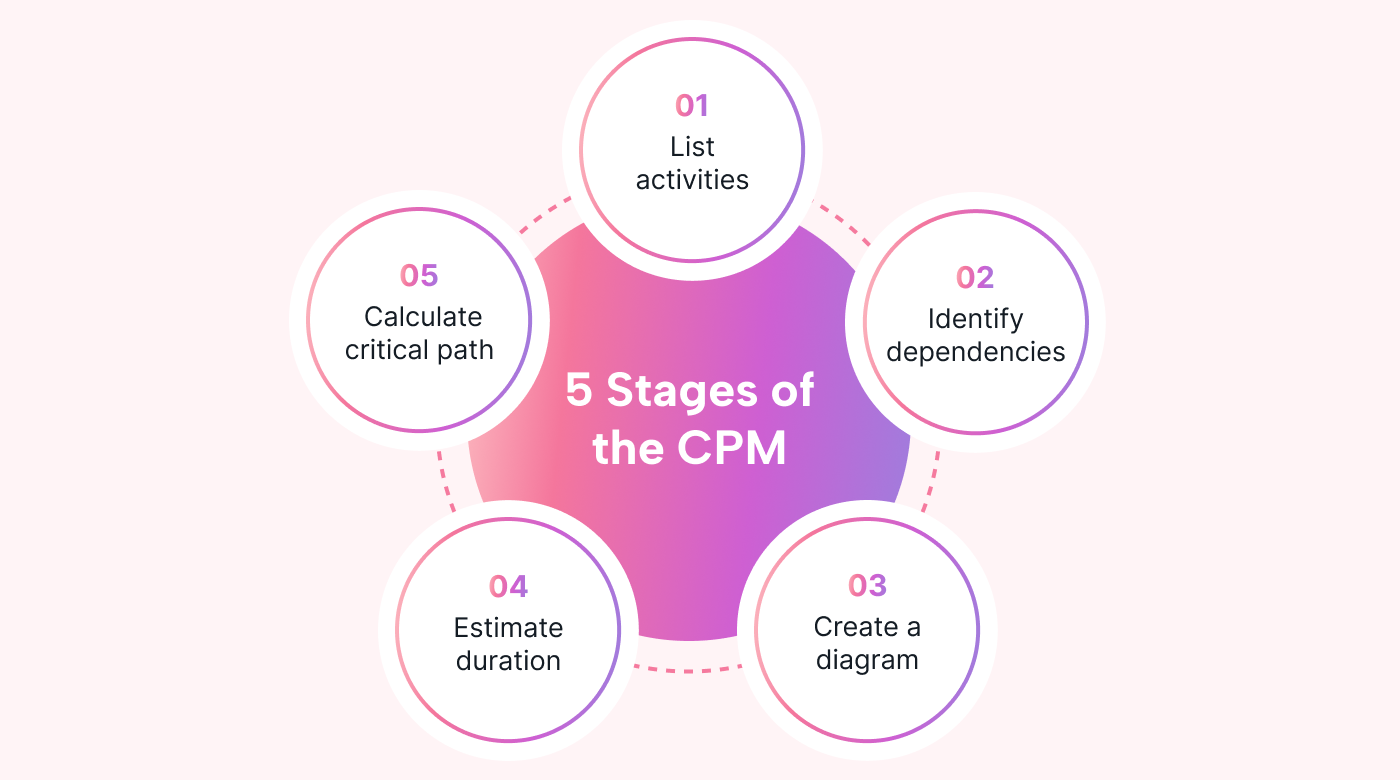 |
List activities
Before you can begin, you need to know all the tasks required to complete your project. The list of tasks is often laid out in the work breakdown structure (WBS), another classic project management technique. This requirement can limit CPM's usefulness because not all project management methodologies can provide a complete list.
Identify dependencies
Before identifying a critical path, you must understand how each task depends on others. Do the two tasks of adding wiring and plumbing actually depend on each other? To use the CPM successfully, you have to know enough to create paths that accurately represent the project.
Create a network diagram
In simple terms, create a flow chart that maps out each path and all the dependencies. More technically, critical path diagrams are usually activity-on-node network diagrams. These diagrams use squares, or nodes, connected by arrows to show a logical sequence of tasks. These graphs provide an easy way to show dependent paths, so it's possible to spot the critical path.
The simplest forms of activity-on-node graphs are easy and intuitive to use. Detailed versions provide different ways of representing different types of precedence relationships.
Estimate task duration
Estimate the time requirements for each task. CPM doesn't offer a method for making those estimates, so you may need to try another tool, like the project evaluation review technique (PERT). You can also investigate more refined techniques that measure effort rather than simple duration. Project management software exists that can also help you make time estimates.
More sophisticated methods estimate time requirements using effort and resource calculations. In other words, they consider each task's expected work hours and the number of workers assigned. It’s a method that is more accurate, and it is often software-assisted.
Calculate the critical path
Once you have the diagram and time requirements for each task, you can identify the critical path and estimate the total time for the project. The total of the durations of tasks on the critical path determines the shortest time required for the project. You can also add information like early and late start times or early and late finish times.
Advantages and drawbacks of the critical path method
The critical path method is a vital tool for most projects. It offers a range of advantages, though it also has some drawbacks.
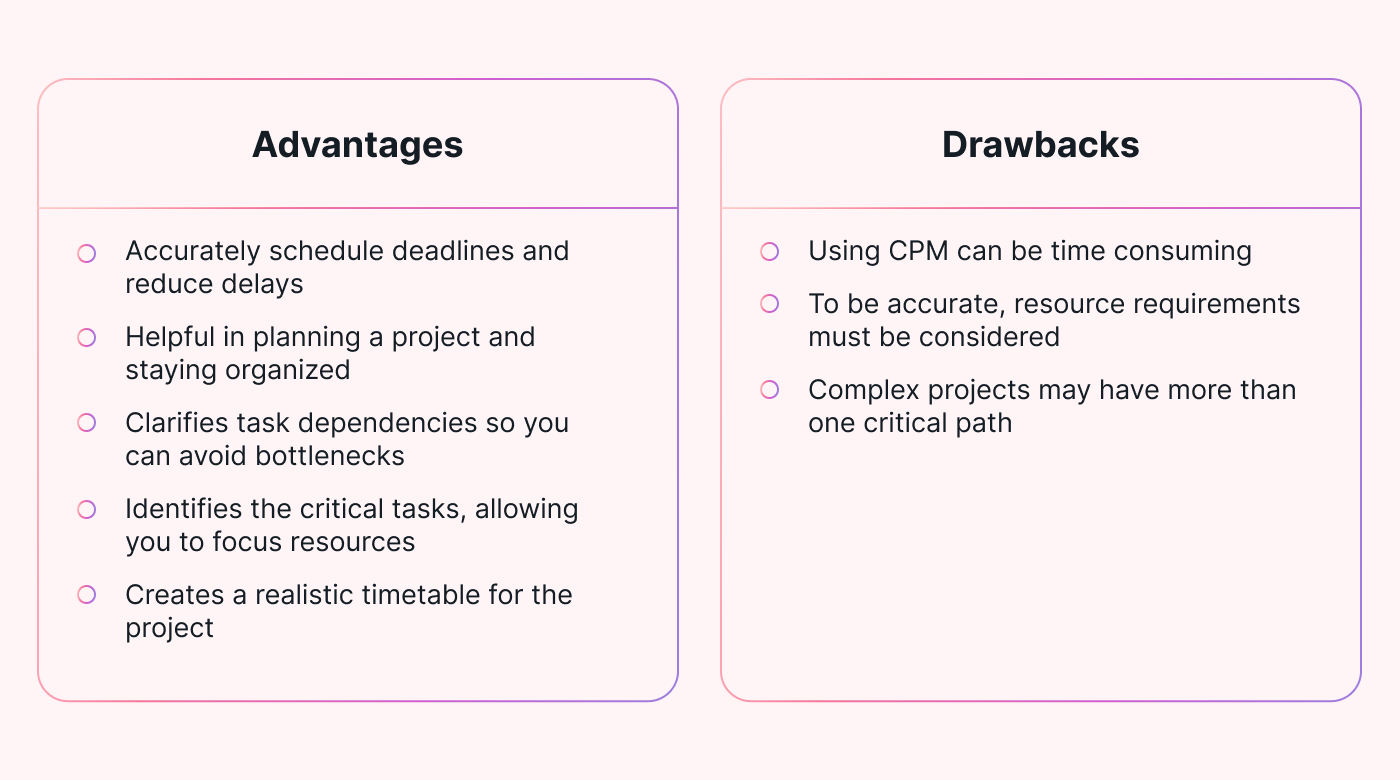 |
Advantages
- Determine the longest path to estimate project duration
- Helpful in planning a project and staying organized
- Clarifies task dependencies so you can avoid bottlenecks
- Identifies the critical tasks, allowing you to focus resources
- Creates a realistic timetable for the project
Drawbacks
- Using CPM can be time-consuming
- Resource requirements must be considered for accurate durations
- Complex projects may have more than one critical path
CPM vs. PERT
Early project managers developed PERT around the same time as CPM. The two methods have some similarities. In particular, they are both concerned with the duration of tasks in a project.
However, the purpose of the two techniques is different. The critical path method assumes you already have time requirements for tasks. On the other hand, PERT is a method of estimating the time requirements of a task.
Moreover, CPM considers only one value for time requirements. PERT provides three estimates, one each for the best, average, and worst-case scenarios.
Critical path examples
Explain a simple example of a critical path analysis for a basic 'project,' cooking a steak dinner. Creating a critical path ensures your steak doesn't sit and get cold while waiting for your side dishes.
1. List activities - Begin by listing out each activity and its time requirements. For our example, we'll use a short list of representative tasks.
a. gather ingredients,
b. chop vegetables,
c. preheat the oven,
d. prepare meat,
e. roast vegetables,
f. cook meat,
g. and serve.
2. Identify dependencies - 'Gather ingredients' has to come first. Then, two paths separate. In one, the oven is preheated, and the vegetables are chopped and then roasted. In the other, the meat is prepared and then cooked. The two join for the final task, serving the food.
3. Create a network diagram - A simple diagram is enough for this example.
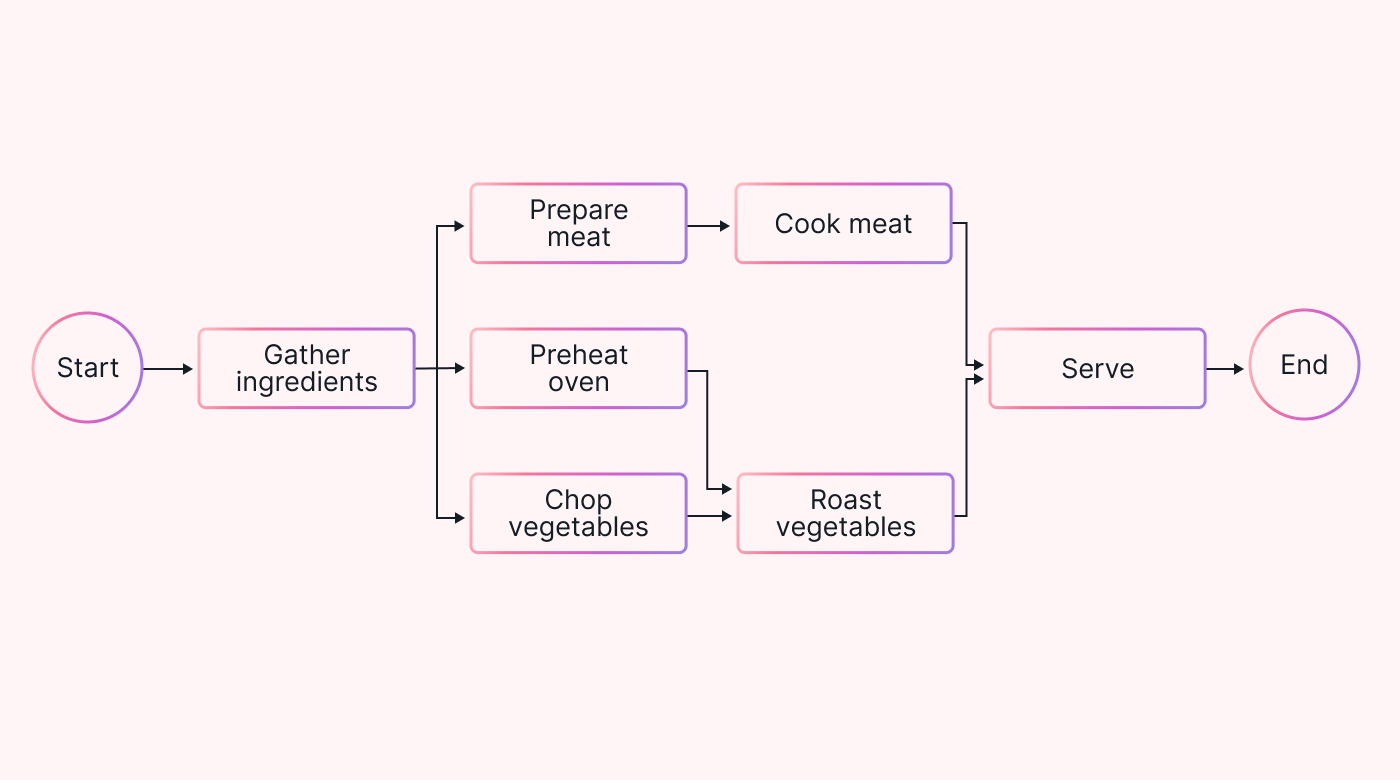 |
4. Estimate task duration - Come up with some estimated numbers using a variety of methods. For our tasks, estimates work out to be:
a. gather ingredients - 5 min,
b. chop vegetables - 10 mins,
c. preheat oven - 5 min,
d. prepare meat - 5 min,
e. roast vegetables - 20 min,
f. cook meat - 10 min,
g. serve - 2 min.
5. Calculate the critical path - In our example, the ‘roasting vegetable’ path takes 37 minutes. The path for cooking the steak took only 22 minutes. Roasting the vegetables is the critical path in this case.
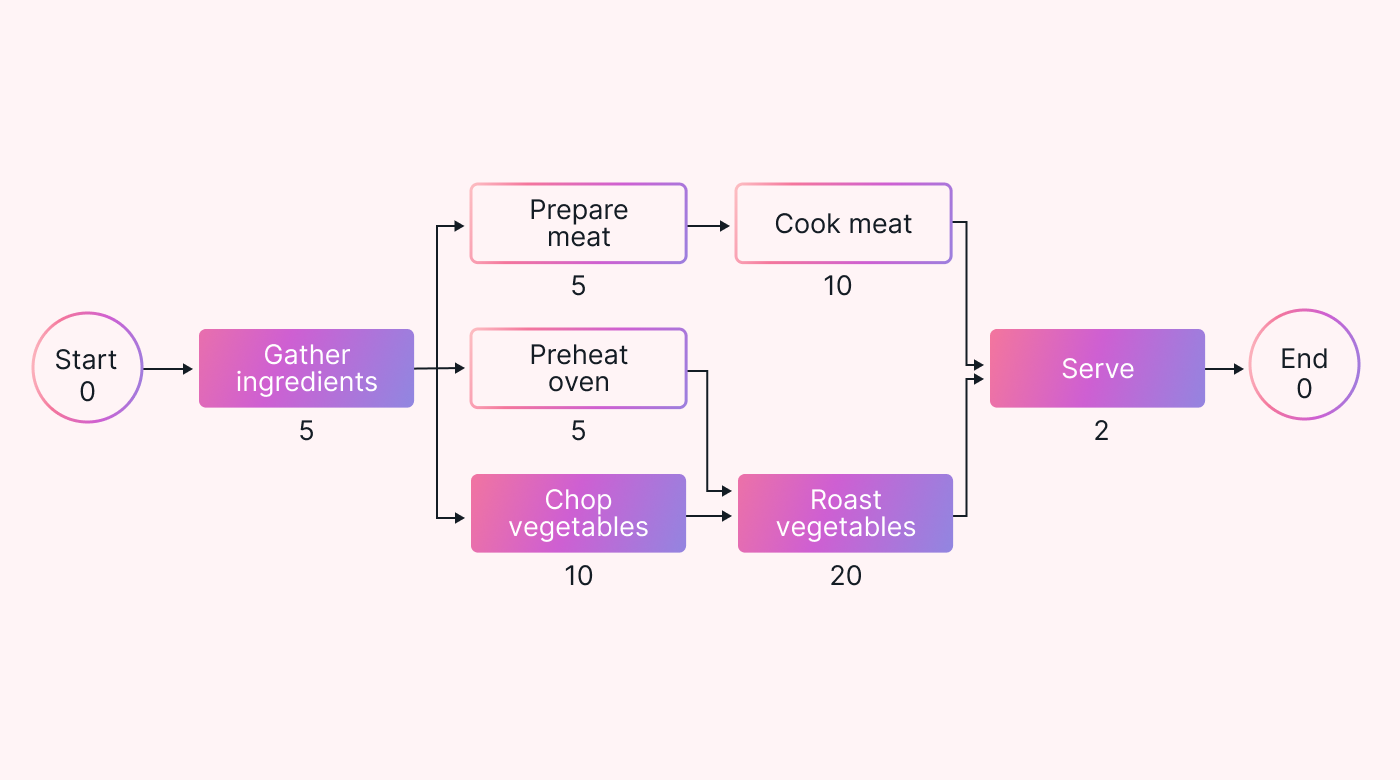 |
A well-done critical path analysis can help you successfully make a delicious dinner with everything getting done in time to serve together. While the steak is the highlight, preparing and roasting the vegetables takes the longest. As a result, the 'roasting vegetables' path determines the shortest time required to project completion.
CPM in waterfall project management
The critical path method is one of the first truly modern tools used in waterfall project management. It might be considered a proof of concept that project management was a separate discipline rather than just a skill that the chief engineer or project administrator should cultivate.
In that sense, CPM helped define waterfall methodologies and works well with a waterfall project management style. Many projects that still predominantly use waterfall methods, like construction, often depend on CPM and similar tools.
CPM in Agile project management
Many classic PM tools from the age of waterfall management can still be useful when an Agile PM methodology is used. However, the critical path method may not be one of them. The CPM depends on a clearly defined list of known requirements and tasks, which Agile projects usually can't provide.
Using iterative work processes, which feature heavily in Agile methods, will also make it difficult to use the CPM. The project team returns to the iterative tasks an unknown number of times, so estimating the total time is difficult.
Use the CPM in your critical projects
In some ways, the development of the critical path method marks the beginning of modern project management. It remains a crucial tool for ensuring a project's success almost a century later. It allows you to set realistic deadlines and helps focus your efforts where they'll do the most good.
Using Motion can help you match a theoretical CPM-determined schedule with your real-life availability and set the most critical tasks to high priority. Motion also allows you to share with teammates, get their input, and complete work on time.